In today’s data-driven landscape, first-party data has emerged as a potent asset for marketers. Its accuracy, relevance, and compliance with privacy regulations make it a powerful tool for understanding customers, personalizing experiences, and driving successful marketing campaigns. Let’s explore the world of first-party data and its impact on modern marketing strategies. 📊
What Is First-Party Data?
First-party data refers to information an organization collects directly from its customers. Unlike second or third-party data from external sources, first-party data is uniquely tied to your business. It is gathered through direct interactions with customers, such as when they fill out lead forms, make purchases, or engage with your website or app. 🛒💻
Why Is First-Party Data Valuable?
Personalization: First-party data allows marketers to personalize their messaging and efforts based on individual preferences, behavior, and demographics. By properly analyzing this data, marketers can enhance their email personalization efforts, recommend more relevant products, services, or content, and deliver seamless, omnichannel experiences. 🎯
Marketing Attribution and ROI Analysis: First-party data enables marketing teams to track and attribute their efforts to specific customer actions or conversions. This data can be used to measure the effectiveness of campaigns, optimize marketing budgets, and more accurately interpret return on investment (ROI). 💰
Cost Savings and Revenue Uplift: A joint 2021 study by Think With Google and Boston Consulting Group revealed that brands using first-party data for key marketing functions achieved up to a 2.9X revenue uplift and a 1.5X increase in cost savings. Despite these clear benefits, many brands have yet to harness first-party data’s full potential.
“Despite its clear benefits […] most brands aren’t yet harnessing first-party data’s full potential.”
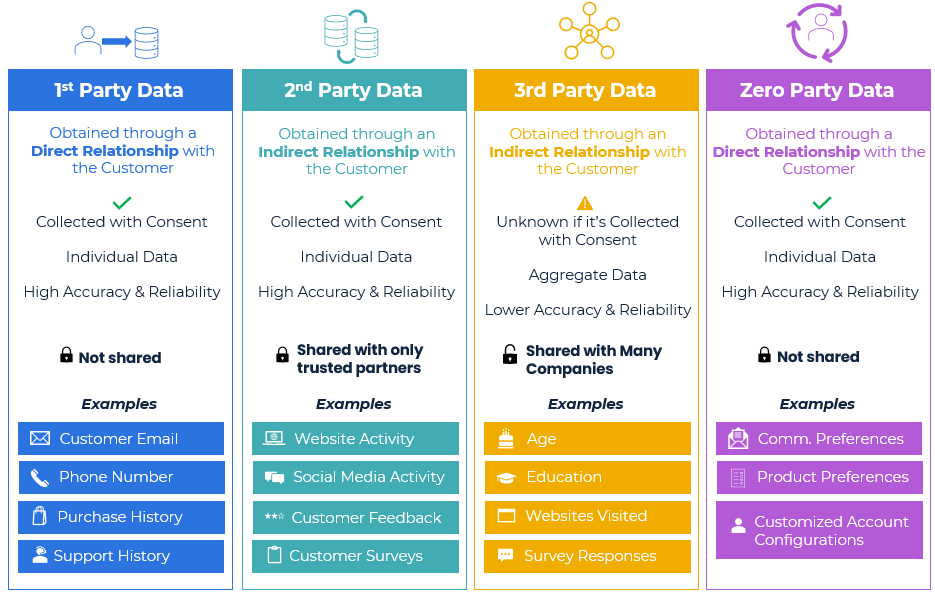
Zero, First, Second, And Third-Party Data Compared
Zero-Party Data: Information that customers knowingly and voluntarily share with a brand. It includes preferences, survey responses, and explicit consent. 📝
First-Party Data: Owned by the organization that collects it, first-party data is generated through direct, one-on-one interactions. Examples include customer profiles, purchase history, and website behavior. 📦
Second-Party Data: Collected by one entity and shared with another trusted partner entity. It provides additional insights and extends the scope of a company’s data for more targeted marketing and audience expansion. 🔄
Third-Party Data: Collected by unaffiliated external entities (data brokers, aggregators, etc.) and typically bought or licensed by companies. It helps with broader audience targeting, market research, and filling gaps in existing data. 📊